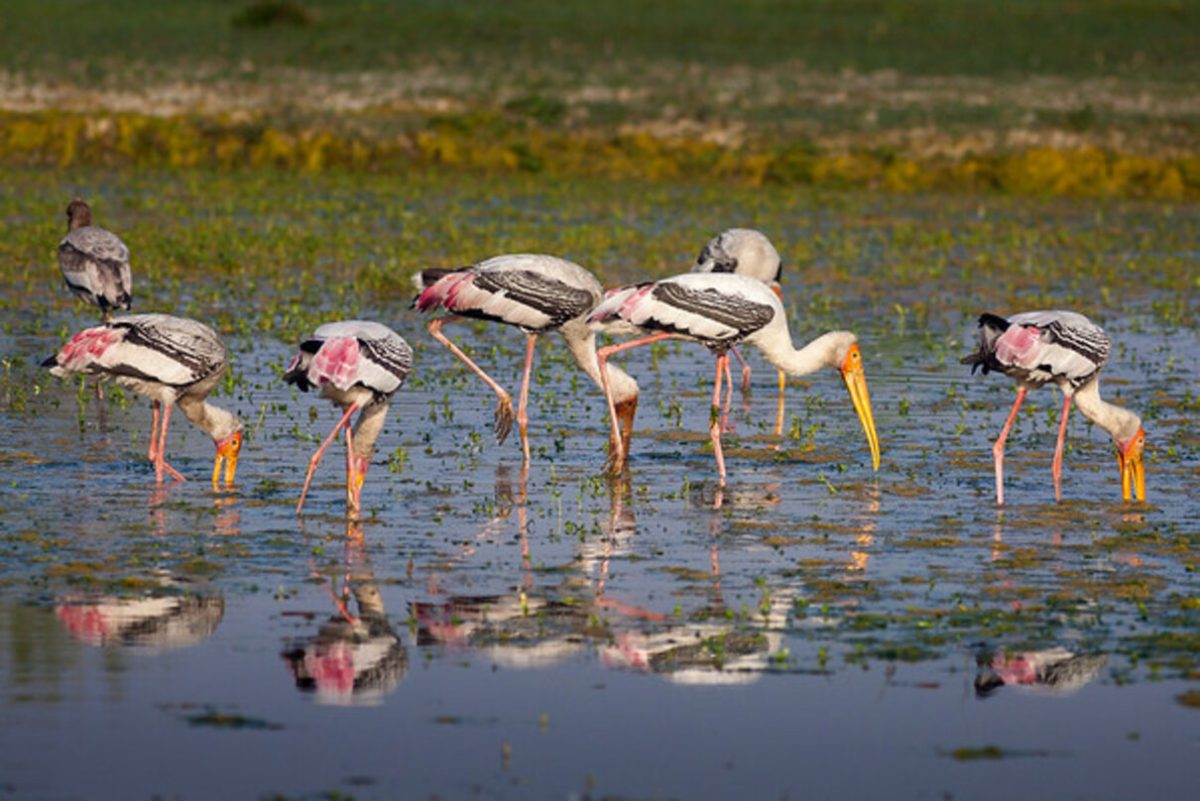
Ramsar Sites in India are the hot news property these days. Why? Because India has recently added three new sites to its list, bringing the total to 85:

- Nanjarayan Bird Sanctuary in Tamil Nadu
- Kazhuveli Bird Sanctuary in Tamil Nadu
- Tawa Reservoir in Madhya Pradesh
So, what are Ramsar Sites? These are vital wetlands recognized globally for biodiversity and ecosystem services. What is the Ramsar Convention? Today I am here to answer this and help you learn more about wetlands sites in India, their importance, and what role we all must play in their protection.
Historical Background of Ramsar Sites:
The Ramsar Convention (Convention on Wetlands of International Importance) has an interesting history. It all started in the 1960s when countries and NGOs began talks to protect wetlands and the resources they offer. The convention was officially signed in 1971 in the city of Ramsar, Iran, and came into effect in 1975. With around 90% of UN member states being part of it, it’s nearly universally accepted.
India joined the convention on February 1, 1982. Its first Ramsar sites were Chilika Lake in Odisha and Keoladeo National Park in Rajasthan. As of August 2024, India has 85 Ramsar Sites, the highest number in South Asia.
The main goals of the Ramsar Convention are to stop the global loss of wetlands. And also, to conserve the ones that remain through wise management. Another goal is to cooperate internationally on shared wetlands, species, and those that cross borders.
How is a Site Designated As a Ramsar Site in India?

India Ramsar Sites are designated based on criteria such as
- supporting rare or endangered species
- biodiversity
- migratory birds
- having unique wetland ecosystems.
- Sites that regulate water cycles or prevent floods also qualify.
These designations are crucial for wetland conservation, as they help protect fragile ecosystems, ensure biodiversity, and preserve endangered species. By maintaining water quality, supporting local livelihoods, and mitigating climate change, Ramsar Sites play an essential role in the long-term conservation of wetlands in India.
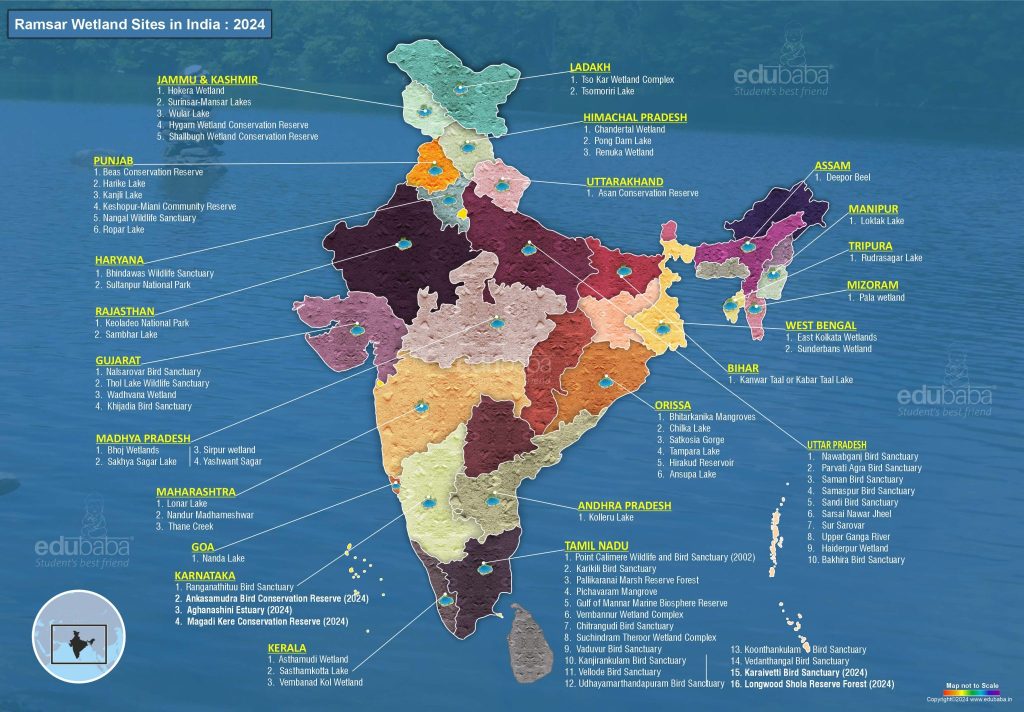
List of 85 Ramsar Sites in India:
| No | Sites | States |
| 1 | Kolleru Lake | Andhra Pradesh |
| 2 | Deepor Beel | Assam |
| 3 | Kanwar Lake | Bihar |
| 4 | Nagi Bird Sanctuary | Bihar |
| 5 | Nakti lake | Bihar |
| 6 | Nanda Lake | Goa |
| 7 | Khijadiya | Gujarat |
| 8 | Nalsarovar | Gujarat |
| 9 | Thol Lake | Gujarat |
| 10 | Wadhvana Wetland | Gujarat |
| 11 | Sultanpur National Park | Haryana |
| 12 | Bhindawas Wildlife Sanctuary | Haryana |
| 13 | Chandra Taal | Himachal Pradesh |
| 14 | Pong Dam Lake Wildlife Sanctuary | Himachal Pradesh |
| 15 | Renuka Lake | Himachal Pradesh |
| 16 | Hokersar Wetland | Jammu and Kashmir |
| 17 | Hygam Wetland Conservation Reserve | Jammu and Kashmir |
| 18 | Shallabugh Wetland | Jammu and Kashmir |
| 19 | Mansar-Surinsar Wildlife Sanctuary | Jammu and Kashmir |
| 20 | Wular Lake | Jammu and Kashmir |
| 21 | Ranganathittu Bird Sanctuary | Karnataka |
| 22 | Ankasamudra Bird Conservation Reserve | Karnataka |
| 23 | Aghanashini Estuary | Karnataka |
| 24 | Magadi Kere Conservation Reserve | Karnataka |
| 25 | Ashtamudi Wetland | Kerala |
| 26 | Sasthamkotta Lake | Kerala |
| 27 | Vembanad-Kol Wetland | Kerala |
| 28 | Tso Kar | Ladakh |
| 29 | Tsomoriri Lake | Ladakh |
| 30 | Bhoj Wetland | Madhya Pradesh |
| 31 | Sakhya Sagar | Madhya Pradesh |
| 32 | Sirpur Lake | Madhya Pradesh |
| 33 | Yashwant Sagar | Madhya Pradesh |
| 34 | Tawa Reservoir | Madhya Pradesh |
| 35 | Lonar Lake | Maharashtra |
| 36 | Nandur Madhameshwar | Maharashtra |
| 37 | Thane Creek | Maharashtra |
| 38 | Loktak Lake | Manipur |
| 39 | Pala Wetland | Mizoram |
| 40 | Ansupa Lake | Odisha |
| 41 | Bhitarkanika Mangroves | Odisha |
| 42 | Chilika Lake | Odisha |
| 43 | Hirakud Reservoir | Odisha |
| 44 | Satkosia Gorge | Odisha |
| 45 | Tampara Lake | Odisha |
| 46 | Beas Conservation Reserve | Punjab |
| 47 | Harike Wetland | Punjab |
| 48 | Kanjli Wetland | Punjab |
| 49 | Keshopur-Miani Community Reserve | Punjab |
| 50 | Nangal Wildlife Sanctuary | Punjab |
| 51 | Ropar Wetland | Punjab |
| 52 | Keoladeo National Park | Rajasthan |
| 53 | Sambhar Lake | Rajasthan |
| 54 | Chitrangudi Bird Sanctuary | Tamil Nadu |
| 55 | Gulf of Mannar Marine Biosphere Reserve | Tamil Nadu |
| 56 | Kanjirankulam Bird Sanctuary | Tamil Nadu |
| 57 | Karaivetti Bird Sanctuary | Tamil Nadu |
| 58 | Karikili Bird Sanctuary | Tamil Nadu |
| 59 | Koonthankulam Bird Sanctuary | Tamil Nadu |
| 60 | Longwood Shola Reserve Forest | Tamil Nadu |
| 61 | Pallikarnai Marsh Reserve Forest | Tamil Nadu |
| 62 | Pichavaram Mangrove | Tamil Nadu |
| 63 | Point Calimere Wildlife and Bird Sanctuary | Tamil Nadu |
| 64 | Suchindram Theroor Wetland Complex | Tamil Nadu |
| 65 | Udhayamarthandapuram Bird Sanctuary | Tamil Nadu |
| 66 | Vadavur Bird Sanctuary | Tamil Nadu |
| 67 | Vedanthangal Bird Sanctuary | Tamil Nadu |
| 68 | Vellode Bird Sanctuary | Tamil Nadu |
| 69 | Vembannur Wetland Complex | Tamil Nadu |
| 70 | Nanjarayan Bird Sanctuary | Tamil Nadu |
| 71 | Kazhuveli Bird Sanctuary | Tamil Nadu |
| 72 | Rudrasagar Lake | Tripura |
| 73 | Bakhira Sanctuary | Uttar Pradesh |
| 74 | Haiderpur Wetland | Uttar Pradesh |
| 75 | Nawabganj Bird Sanctuary | Uttar Pradesh |
| 76 | Parvati Arga Bird Sanctuary | Uttar Pradesh |
| 77 | Saman Bird Sanctuary | Uttar Pradesh |
| 78 | Samaspur Bird Sanctuary | Uttar Pradesh |
| 79 | Sandi Bird Sanctuary | Uttar Pradesh |
| 80 | Sarsai Nawar Jheel | Uttar Pradesh |
| 81 | Sur Sarovar | Uttar Pradesh |
| 82 | Upper Ganga River | Uttar Pradesh |
| 83 | Asan Barrage | Uttarakhand |
| 84 | East Kolkata Wetlands | West Bengal |
| 85 | Sundarban Wetland | West Bengal |
Ecological and Biodiversity Importance of Ramsar Sites in India:

India’s Ramsar Sites are wetlands that are recognized for their ecological and biodiversity importance. They are vital habitats for many species of plants, birds, and other wildlife. They also play a key role in water conservation, flood control, and climate regulation.
Here are some of the ecological and biodiversity importance of India Ramsar Sites:
- Ramsar Sites are important habitats for birds, aquatic life, and various plants. For instance, the Longwood Shola Reserve Forest in Tamil Nadu is home to the endangered Black-chinned Nilgiri Laughing thrush.
- These sites help conserve water, recharge aquifers, and provide water for drinking and farming.
- Wetlands also store large amounts of carbon, playing a key role in climate action.
- Ramsar Sites support local communities by providing resources and livelihoods and promoting tourism.
- Designating a site as a Ramsar site brings international attention, which can lead to increased funding and support for conservation efforts.
Economic and Social Benefits of Ramsar Sites in India:

By protecting biodiversity and natural resources, India Ramsar Sites support sustainable development and improve the quality of life for people. Wetland sites in India provide vital economic benefits by supporting livelihoods through:
- fishing, farming, and tourism, creating income for local communities.
- naturally filter water, reducing the need for costly water treatment facilities.
- help in flood control and disaster recovery.
- Socially, these sites preserve cultural heritage and offer spaces for recreation, education, and tourism.
- promote environmental awareness in local and global communities.
Read More: 10 Wildlife Sanctuaries & National Parks of India
Conversation Challenges Faced by Ramsar Sites in India:

Wetlands are crucial for biodiversity, supporting about 40% of all plant and animal species, even though they cover just 6% of the Earth’s land. Unsustainable development is a major threat to Ramsar sites, as unplanned urban and agricultural expansion continues to grow. This includes building dams, canals, and reservoirs without proper impact studies. Climate change adds further pressure, with rising temperatures, sea levels, and extreme weather events making wetlands more vulnerable. Pollution is another concern, with industries and households polluting wetlands. The spread of invasive plants like water hyacinth and Salvinia also poses a risk. Unplanned Tourism, which is when not managed properly, can harm local ecosystems and communities. Wetlands have also been neglected in national water policies and sometimes government projects contribute to their destruction.
Government and Community Efforts for the Ramsar Wetlands in India:
Unfortunately, India has lost around 30% of its natural wetlands in the last thirty years, highlighting the urgent need for conservation efforts.
Communities play a big part in taking care of wetlands. Local people are getting more involved in activities that help protect these areas, like promoting eco-tourism and spreading awareness. They work together with the government, local leaders, and environmental groups to make sure Ramsar sites are kept safe. This teamwork helps keep Ramsar wetlands in India healthy and supports the people living nearby with jobs and resources. Recently, the government has added new Ramsar sites, like Nanjarayan and Kazhuveli Bird Sanctuaries in Tamil Nadu, and Tawa Reservoir in Madhya Pradesh. Prime Minister Modi also said that protecting nature and wetlands is a big goal for the government. The government has launched several programs aimed at wetland conservation, including the National Plan for Conservation of Aquatic Ecosystems (NPCA).
Case Studies of 2 Latest Ramsar Sites in India:
1. Kazhuveli Bird Sanctuary, Tamil Nadu:

Kazhuveli Bird Sanctuary also received Ramsar Site status in August 2024. This site spans around 4,400 hectares and is important for both resident and migratory birds. The wetlands here help control flooding and maintain water quality in the area. The government and local organizations work together to raise awareness and protect this sanctuary, ensuring its ecological health.
2. Tawa Reservoir, Madhya Pradesh:

Tawa Reservoir was added to the Ramsar list in August 2024. It covers approximately 2,675 hectares and is vital for fish and various bird species, contributing to local fishing activities. However, it faces challenges like pollution and invasive species that threaten its ecosystem. The government is taking steps to restore and manage the habitat to protect this important site.
Important Steps to Protect Ramsar Sites in India:
Now that we have understood a lot about Wetland sites in India, thus I now want to talk about the important steps we can take to protect our wetlands in India.
- First, it’s crucial that we prioritize the conservation and management of specific wetland sites. The Indian Ministry is already doing this by providing financial support to ensure these areas are well taken care of.
- Next, we need to develop effective management plans. The Ramsar Sites management toolkit offers guidance on this. It emphasizes the importance of having clear management plans, monitoring programs, and training for staff who work at these sites.
- Involving stakeholders is also vital. The Fourth Convention Strategic Plan for 2016–2024 encourages the participation of various groups, including local communities and indigenous peoples. Their knowledge and involvement can greatly enhance conservation efforts.
- We should also promote ecotourism. Wetlands sites in India can support sustainable tourism, which not only creates jobs but also helps showcase local culture and products. This can be a win-win situation for both the environment and the economy.
- However, we must consider the impacts of climate change on Ramsar wetlands in India. Increased temperatures, shifts in rainfall patterns, and rising sea levels can make wetlands more vulnerable. We need to be aware of these changes and adapt our conservation strategies accordingly.
- Ultimately, conducting scientific studies is essential. These studies provide valuable insights that can help make our conservation efforts more effective.
- Lastly, creating funding opportunities will play a critical role in supporting these conservation initiatives. With adequate funding, we can implement all the necessary actions to protect our wetlands.
In conclusion:
I would just like to add that the theme for World Wetlands Day 2024, “Wetlands and Human Wellbeing,” highlights the essential benefits wetlands provide. Thus, as Indians and tourists, a whole lot of responsibility lies on us also, to keep them clean and safe.
FAQs:
Ramsar Sites in India are wetlands of international importance designated under the Ramsar Convention, aiming to conserve and sustainably use these ecologically significant areas.
As of 2024, India has 85 Ramsar Sites, covering a wide range of wetland ecosystems across the country.
A site can be designated as a Ramsar Site if it meets one or more criteria, including supporting rare species, hosting significant numbers of migratory birds, or having unique wetland ecosystems.
Ramsar Sites provide resources like fish, water, and materials, support tourism and recreational activities, and contribute to the livelihoods of millions, especially in rural areas.









